Cases
Targeted Protein Degradation Technology - Antibody PROTAC (AbTAC)
Background:
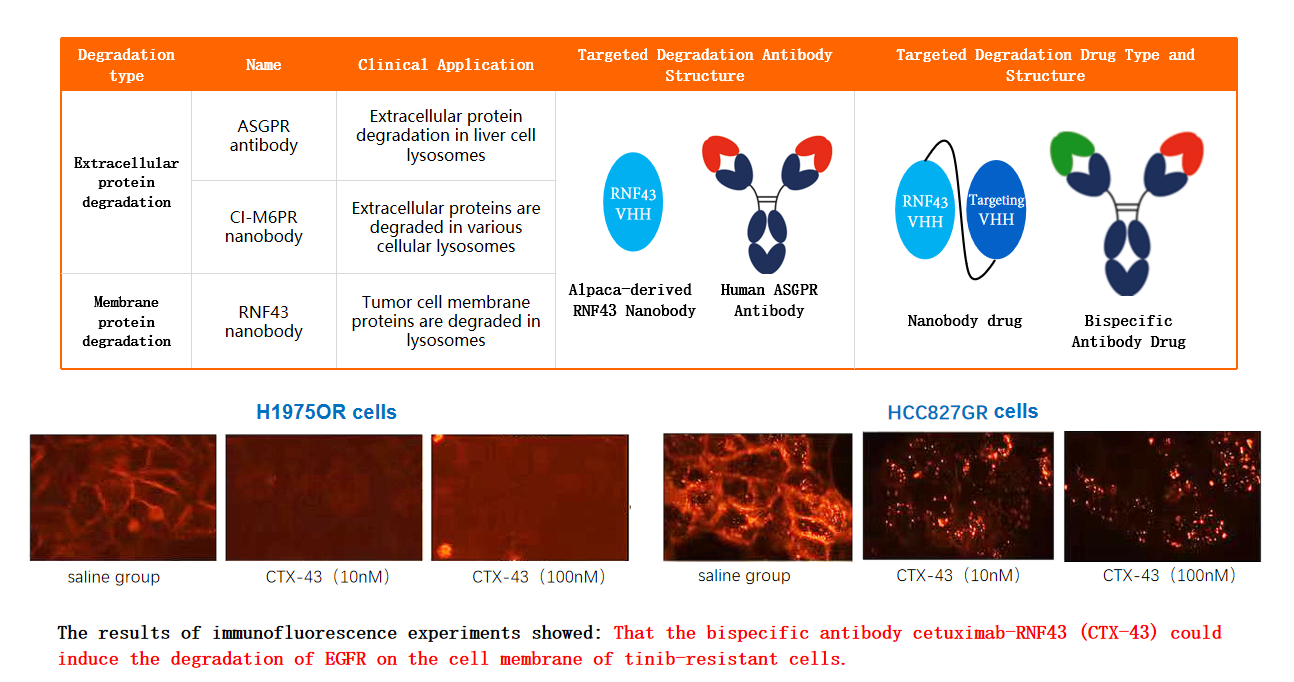
The AbTAC technology is based on the concept of proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTACs). A PROTAC molecule contains two ligands linked by a linker, one of which can specifically bind to a target protein, and the other binds to an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Therefore, the PROTAC molecule can recruit E3 ubiquitin ligase to polyubiquitinate the target protein and then degrade it through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. This technology has good effects in treating diseases caused by protein overexpression or mutation, while the AbTAC technology utilizes the properties of bispecific antibodies to develop monoclonal antibodies that can simultaneously target both the target protein and the E3 ubiquitin ligase (such as RNF43). ABLINK has developed nanobody drugs and human ASGPR antibody drugs that can execute extracellular protein and membrane protein degradation. CTX-43 is an example of a bispecific antibody that can target the RNF-43 and EGFR membrane proteins. EGFR is thought to be associated with malignant tumors. Immunofluorescence experiments have shown that CTX-43 can induce EGFR degradation on H19750R cells resistant to the EGFR inhibitor osimertinib and HCC827GR cells resistant to gefitinib.