Cases
Shuttle Antibody Technology
Background:
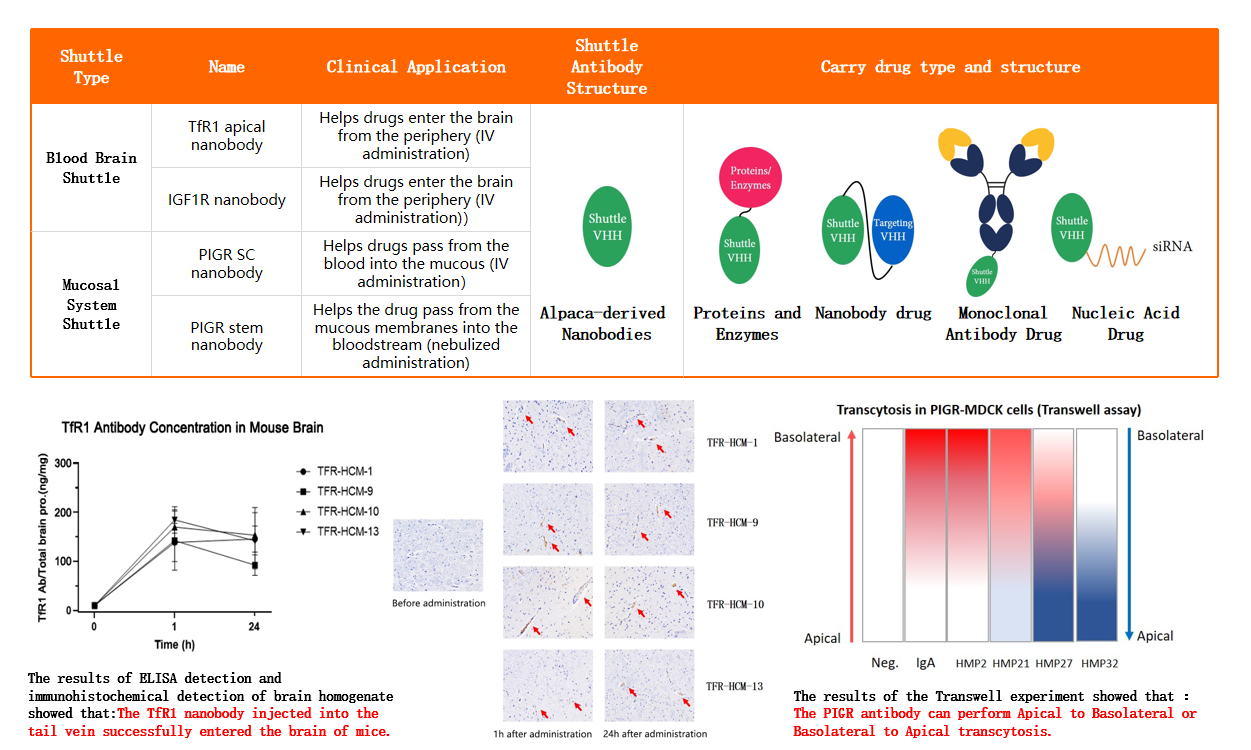
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective and semi-permeable boundary formed by brain endothelial cells (BECs) and capillary walls, which separates the bloodstream from brain cells. While the BBB protects the brain tissue from harmful substances, it also makes it difficult to develop therapeutic antibodies for central nervous system diseases. Antibodies that can cross the BBB are known as shuttle antibodies. There are various transport pathways for crossing the BBB, among which receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) that utilizes vesicle-mediated transport is the primary pathway for shuttle antibodies. Among the RMT receptors highly expressed in BECs, transferrin receptor (TfR) is the most studied, and ABLINK has also studied shuttle antibodies against IGF1R. Based on these two antigens, ABLINK screened suitable camel-derived nanobodies. During the screening process, optimal affinity with RMT receptors needs to be considered, as high-affinity antibodies that bind too strongly to receptors are easily trapped in vascular attachments and have a short half-life due to their ease of clearance in the periphery, where TfR and IGF1R are widely expressed. The choice of antigenic epitopes also needs to be considered to avoid competition between the antibody and transferrin binding, which can affect receptor function. The screened antibody needs to be validated for crossing the BBB by ELISA and immunohistochemistry assays on brain homogenate. Shuttle antibodies can be linked with different molecules (enzymes, antibodies, RNA, etc.) to exert different effects, such as shuttle antibodies linked with anti-beta-amyloid antibodies that have potential therapeutic effects for Alzheimer's disease. ABLINK also studied shuttle antibodies that can shuttle through the mucosal system.