Cases
Antibody Humanization (AI-Assisted Design)
Background:
Non-human antibodies entering the human body can cause serious immune rejection reactions, thereby affecting the safety and therapeutic effect of antibodies in clinical applications. In clinical research, there are often cases where the efficacy is reduced and adverse reactions occur due to drug-resistant antibodies, which have resulted in many years of product development being declared as failures. Antibody humanization modifies animal-derived antibodies through genetic engineering to give them a structure similar to that of human antibodies, thus avoiding recognition by the immune system. ABLINK's antibody humanization service combines computer simulation, phage display library screening and AI-assisted design technologies, achieving a humanization rate of over 90%.
Process:
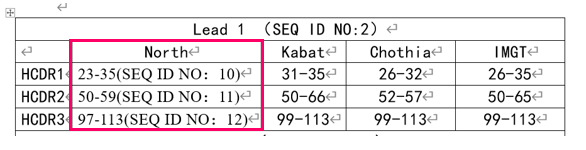
1. CDR clustering:
By sequencing the parent non-human antibody gene, ABLINK can analyze the VH and VL sequences of the parent antibody, subtype classification, computer simulation antibody structure analysis, and multiple sequence alignment to locate the CDR region and framework region.
2. Homology template selection and CDR transplantation:
Search for an antibody V-region homologous protein to determine the template protein structure and sequence, and transplant the parent antibody CDR region to the template antibody.
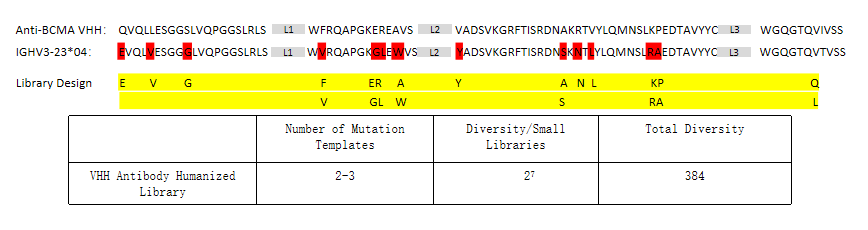
3. Mutant library construction:
Through comparative analysis of the parent non-human antibody and the template human antibody, determine the conserved amino acids and key amino acid residues and their positions in the framework region, and identify mutation sites. Build a mutant library using the Kunkel method and phage display.
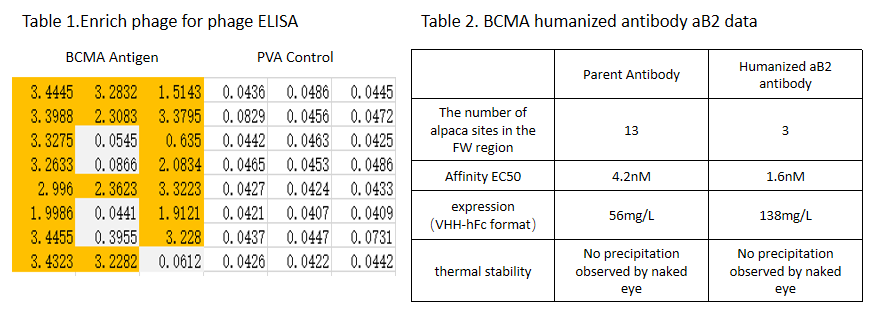
4. Screening and validation:
Screen and enrich high-affinity antibodies and use ELISA to validate (Table 1). The resulting humanized antibodies have higher humanization rates, stronger affinity, and higher expression levels compared to the parent antibodies (Table 2).