Cases
NGS-assisted High-Affinity Antibody Screening (AI Data Mining)
Background:
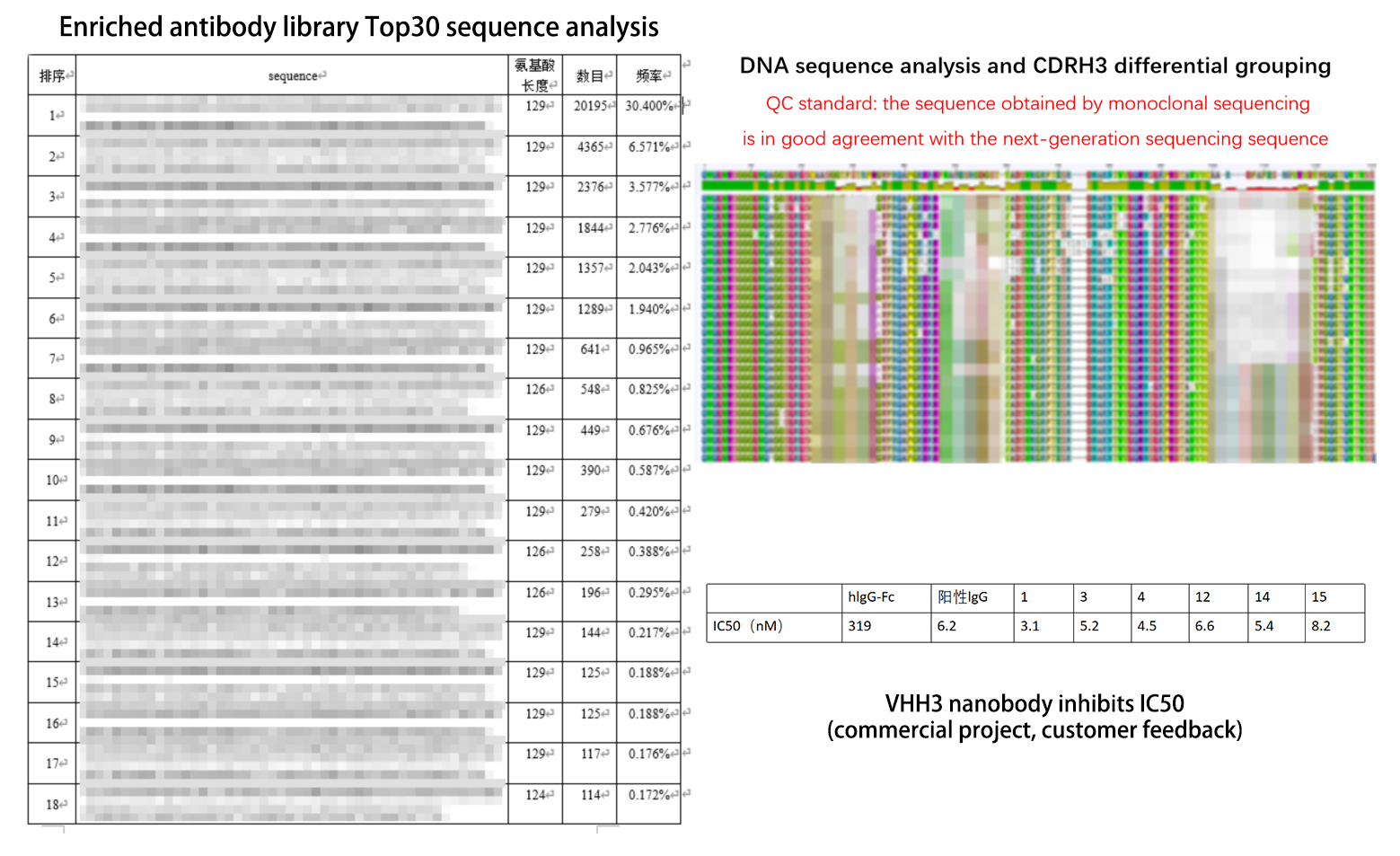
Next-generation sequencing (NGS), also known as high-throughput sequencing technology, is capable of sequencing hundreds of thousands to millions of nucleic acid molecules in a single run, compared to the traditional Sanger sequencing method. The development and maturation of NGS sequencing technology has made it possible to systematically analyze antibody gene sequences, especially those from large and diverse antibody libraries. Currently, all display technologies used for library screening rely on a principle of phenotype selection pressure, i.e. depending on the competitive binding strength between receptor and ligand. While this screening process enriches target antibody genes through display technology, it may also miss some rare molecules, low-affinity molecules, molecules with low soluble expression, or low-yielding antibody genes in the screening process. On the other hand, DNA sequencing processes have no selection pressure and can release more complete sequence information of the gene library, which is advantageous for capturing target genes.
Service Process:
Utilizing its high-throughput capabilities, NGS sequencing can obtain gene sequences of tens of thousands of positive monoclonal antibodies screened through 3-5 cycles. For these sequences, bioinformatics analysis divides them into groups based on their differences in the CDR regions, and one or two clones are selected for expression validation in each group. Based on the validation results and practical needs, appropriate groups are selected and the other sequences within the groups are also validated. For the screened target antibodies, stable antibodies can be obtained by recombinant protein expression after obtaining their coding sequences.