Cases
Antibody-Blocking Peptides (AI Affinity Prediction)
Background:
Blocking peptides are peptides that specifically bind to target antibodies and block their binding ability. These peptides usually contain epitopes recognized by the antibody, and antibodies that bind to blocking peptides no longer bind to epitopes on the target protein. When some antibodies cause peripheral toxicity due to their non-specific binding, blocking peptides can be used to block the antibody and, when the antibody reaches the tumor site, the peptide is cleaved by enzymes and the active portion of the antibody is exposed, killing tumor cells.
Process:
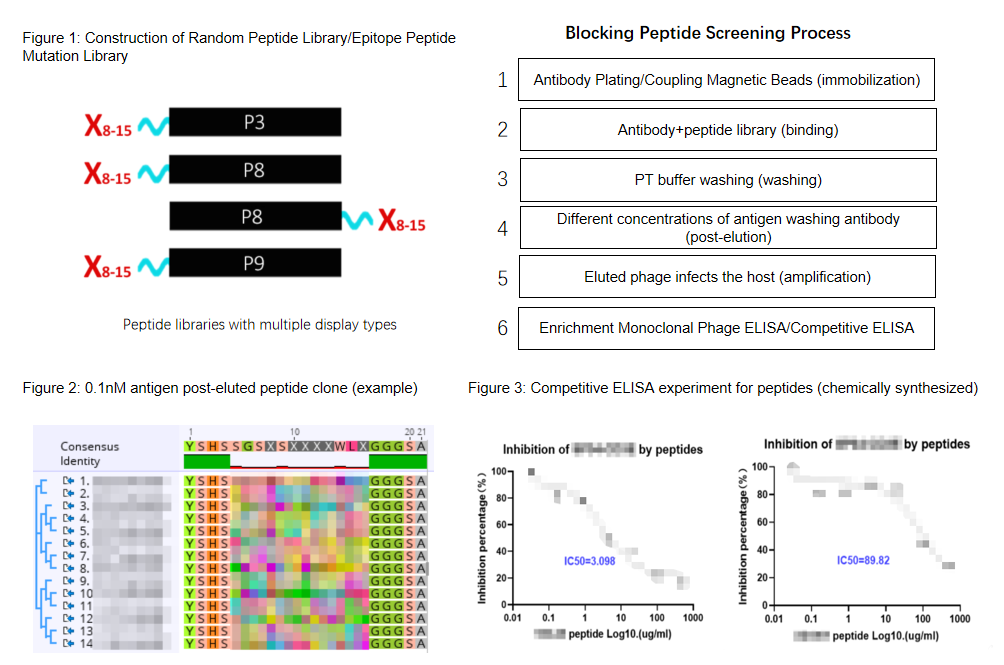
The screening of blocking peptides requires the construction of a random peptide library. ABLINK uses NNK degenerate primers to construct a random peptide library and allows for the construction of linear and cyclic peptide libraries. The peptides can also be linked to different proteins on phages (Figure 1).
One major requirement for the screening of blocking peptides is their appropriate affinity. Blocking peptides with too high an affinity permanently bind to the antibody, making it difficult to detach, while those with too low an affinity are easily detached before the antibody reaches the tumor site. Therefore, in the elution step of blocking peptide screening, different concentrations of antigen are used to wash the antibody (Figure 2). The enriched clones are then validated through ELISA/Competitive ELISA after amplification (Figure 3), and peptides with appropriate IC50 values are selected.